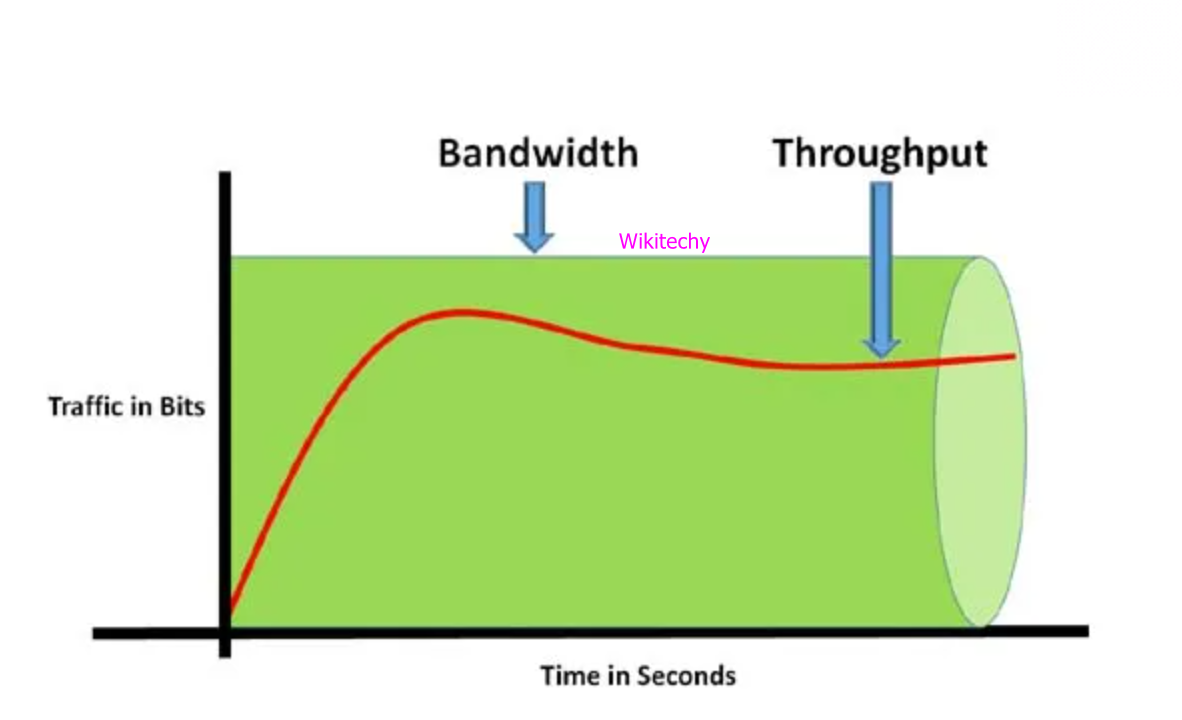
- It is used to measure the maximum capacity of a wired or wireless communications link to transmit data over a network connection in a given amount of time.
- Every signal has a limit of lower range frequency and upper range frequency.
- Bandwidth is typically represented in the number of bits, kilobits, gigabits or megabits that can be transmitted in 1 second.
- It is typically done using firmware or software and a network interface.
- Bandwidth commonly measures utilities include the Test TCP utility (TTCP) and PRTG Network Monitor.
- In this utilities TTCP measures throughput on an IP network between two hosts and PRTG can measure traffic between different interfaces then provides a graphical interface and charts for measuring bandwidth trends over longer periods of time.
- To measure the bandwidth by the total traffic sent and received across a specific period of time is counted.
- It is usually measured in bits transferred per second through a link or path.
- There are common units bandwidth are as follows Bits Per Second(BPS), Megabits Per Second (MBPS), Gigabits Per Second (GBPS).