What is Authorization ?
What is Authorization ?
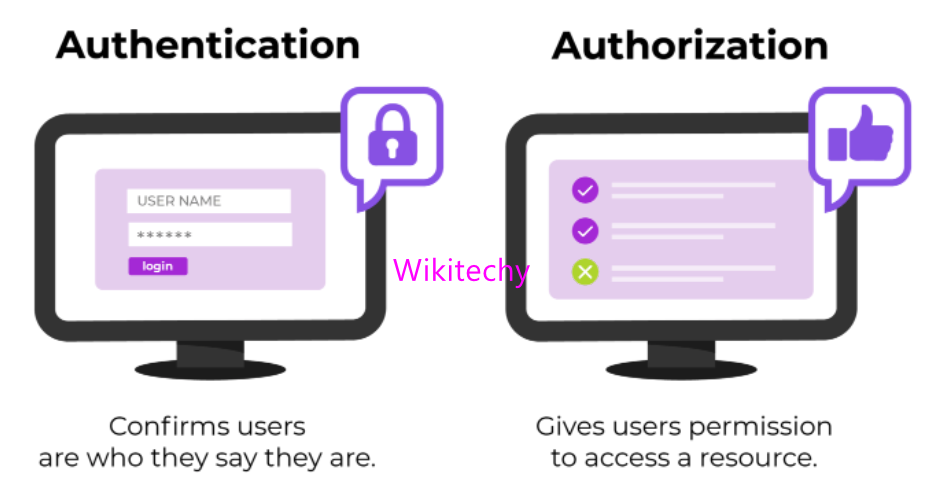
Table Of Content
- Authorization is a security mechanism to determine access levels or user/client privileges related to system resources.
- Including files, services, computer programs, data and application features.
- This is the process of granting or denying access to a network resource which allows the user access to various resources based on the user’s identity.
- There are two types of authorization
- Server-side Authorization
- Client-side Authorization

Server-side Authorization
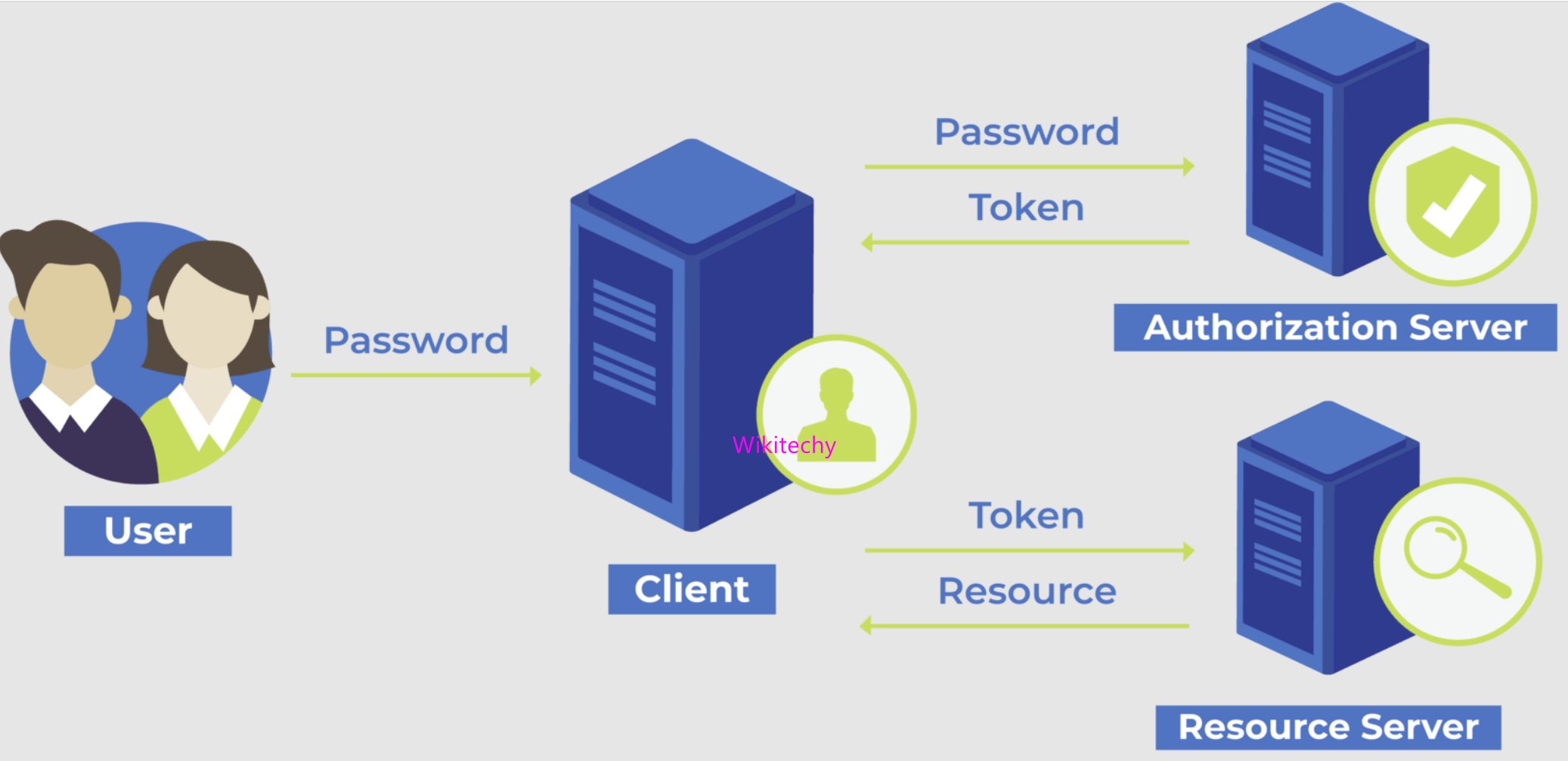
- The server has three authorization modes. Depending on the authorization mode we choose, the server will decide if it accepts or declines an incoming invocation.
None
- This is the simplest type of authorization. No authorization will be performed.
Self
- A client will be allowed to use a grid service if the client’s identity is the same as the service’s identity.
Gridmap
- A gridmap is a list of ‘authorized users’ akin to an ACL (Access Control List).
- When this type of authorization is used, only the users that are listed in the service’s gridmap may invoke it.
Client-side Authorization
- This allows the client to figure out when it will allow a grid service to be invoked.
- This might seem like an odd type of authorization, since authorization is generally seen from the server’s perspective (“Do I allow client FOO to connect to grid service BAR?”).
- However, in GSI, clients have every right to be picky about the services they can access.
None
- No authorization will be performed.
Self
- The client will authorize an invocation if the service’s identity is the same as the client.
- If we use both client-side and server-side Self authorization, a service can be invoked if and only if its identity matches the client’s.
Host
- The client will authorize an invocation if the host returns an identity containing the hostname.
- This is done using host certificates.