There are 7 keys in DBMS
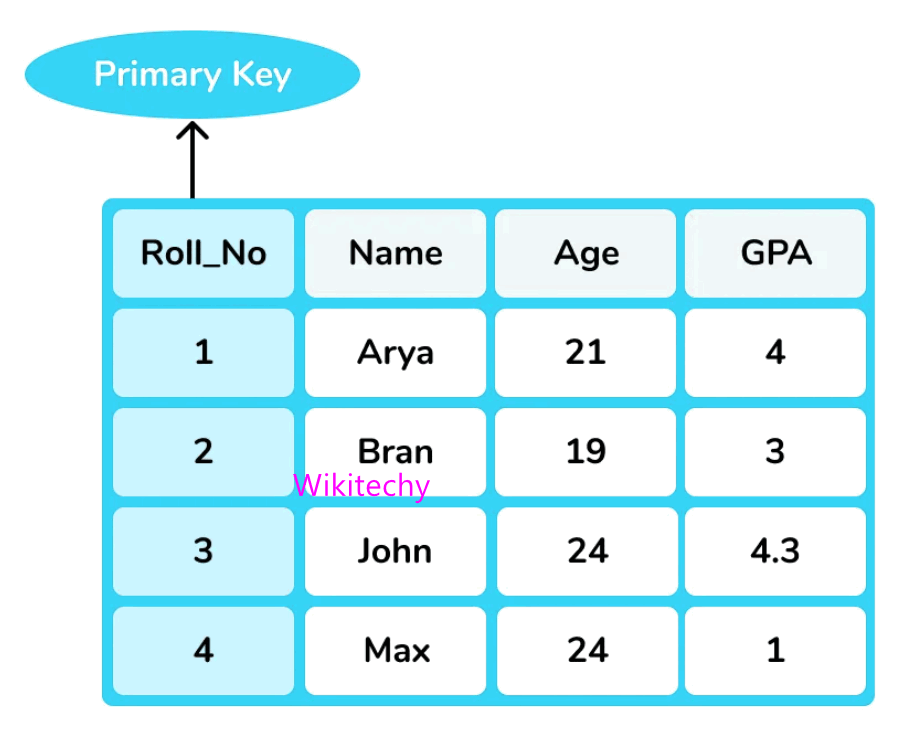
Primary Key
- Key which is used to identify one and only instance of entity uniquely. An Enity can contains multiple keys, and keys which is most suitable becomes the primary key.
- For each entity the primary key selection is based on requirements and developers.
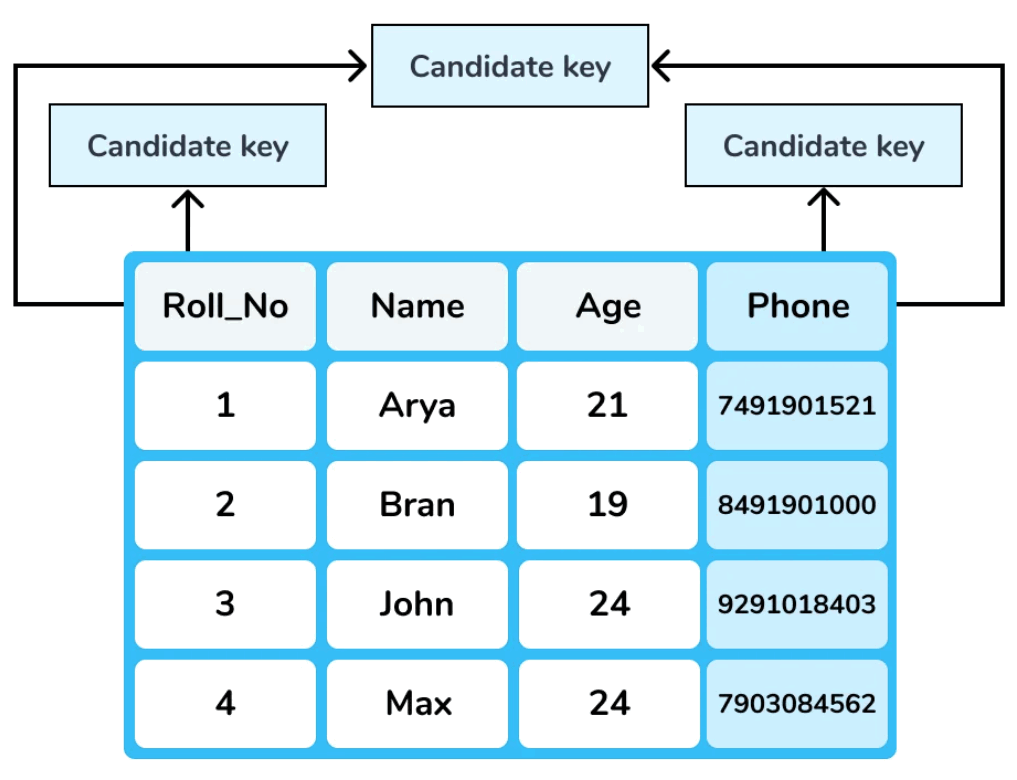
Candidate Key
- A key or an attribute that uniquely identifies a tuple is called Candidate key.
- Apart from primary key, other keys are considered as candiate key.
- The candidate keys are as strong as the primary key.
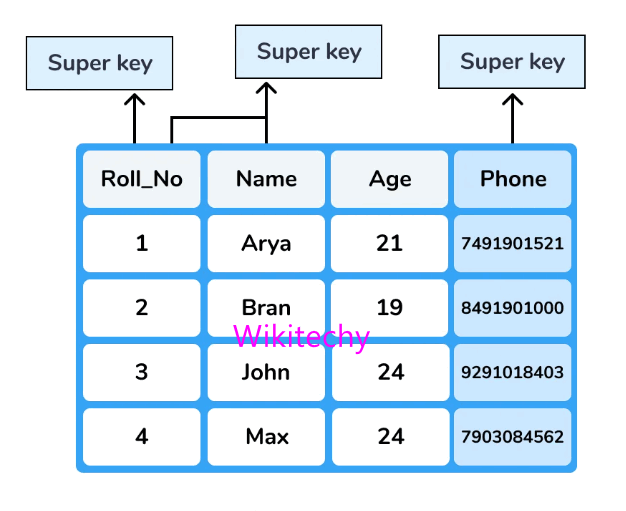
Super Key
- An attribute set that can uniquely identify a tuple is called as Super Key. It is a superset of candidate key.
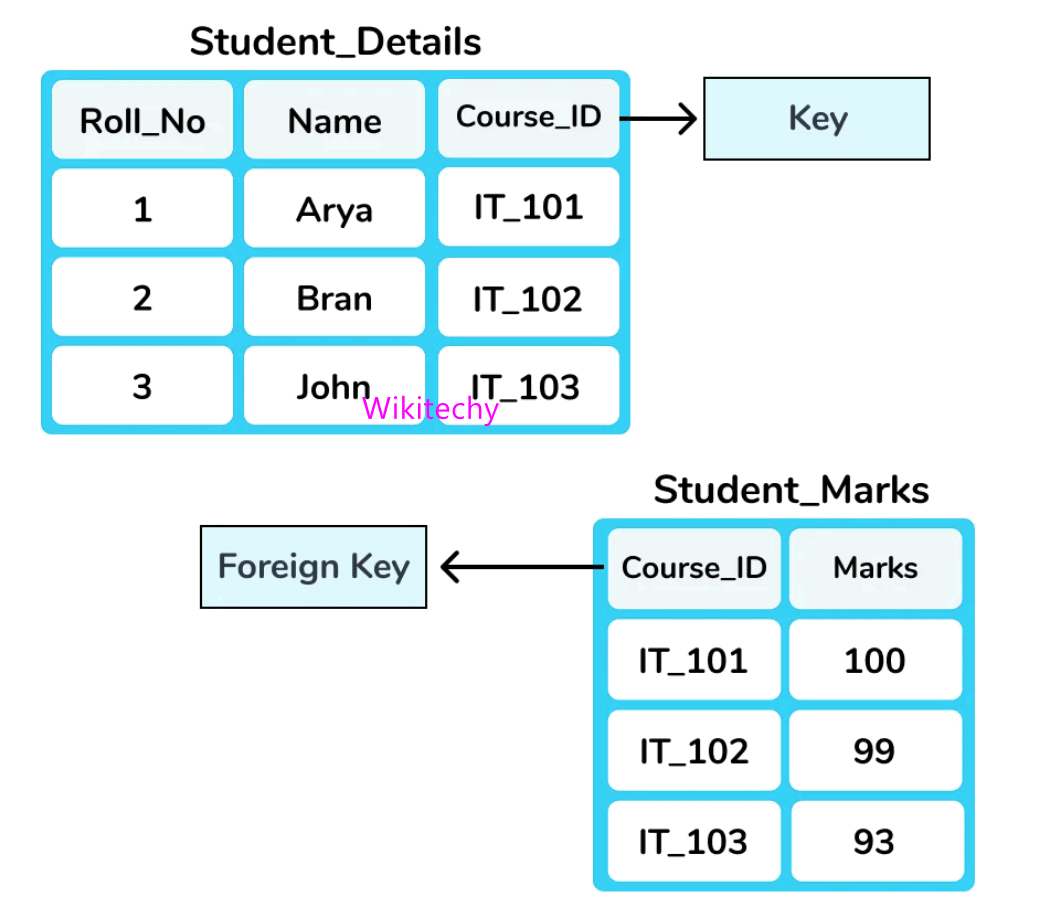
Foreign Key
- Column of table that is used to point the primary key of another table is called as Foreign key.
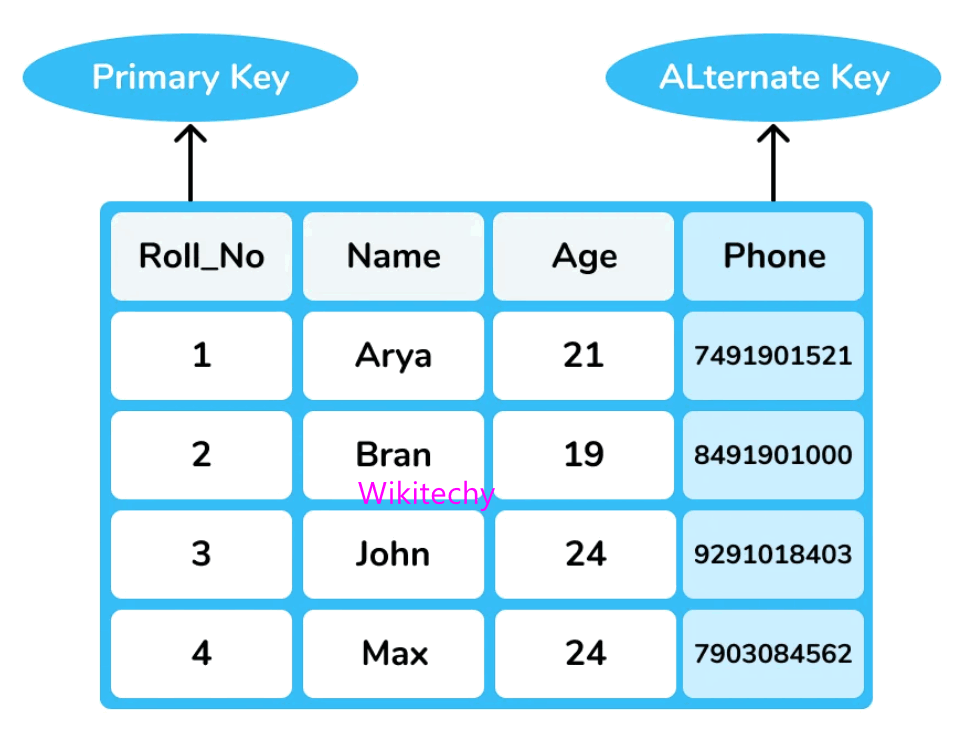
Alternate Key
- One of more attributes or a combination of attributes that uniquely identifies a tuples in a relation is called Alternate Key.
- These attributes or combinations of the attributes are called the candidate keys.
- One key is chosen as primary key and the other keys remain as candidate keys if they exist and is called as alternate keys.
- Total number of alternate keys is the total number of candidate keys minus the primary key.
- In a relation if there is only one candidate key alternate keys may or may not exist.
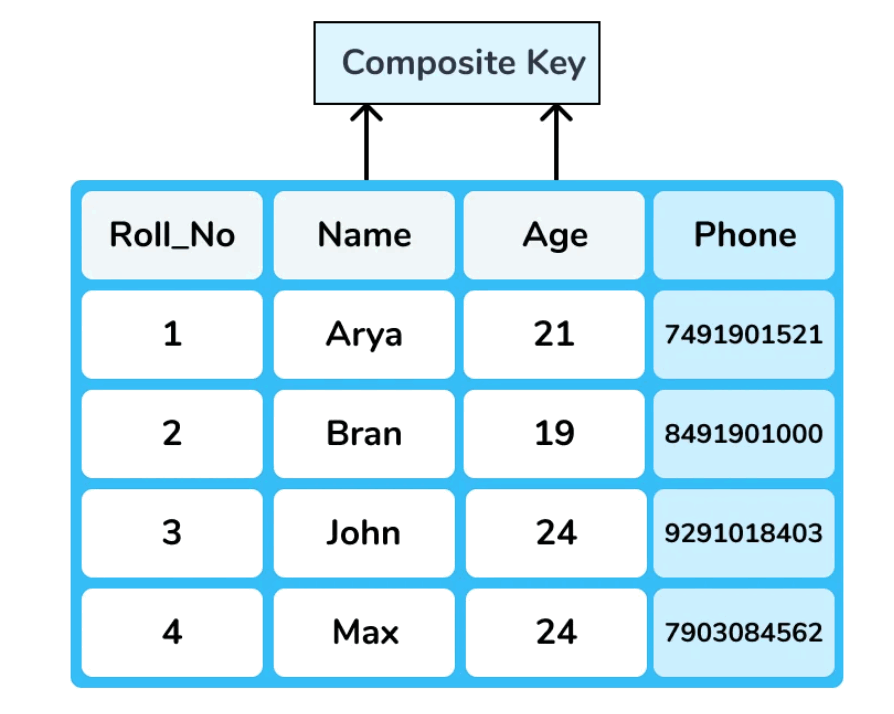
Composite Key
- Whenever there is more than one attribute in a primary key, it is known as Composite key or concatenated key.
Artificial Key
- Keys that are created using arbitarily assigned data is known as artificial keys.
- When primary key is large and complex and has no relationship with other relations, then the artificial key is created.
- Data values of an artificial key are usually numbered in serial order.

