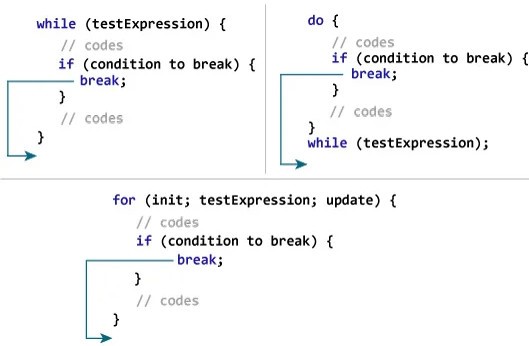
Break
- This statement is used with switch statement.
- Can also be used with while loop, do – while loop and for loop.
- When the control encounters a break statement, the control will terminate the loop immediately and the statements after break will not be executed.
Syntax
Sample Code
Output

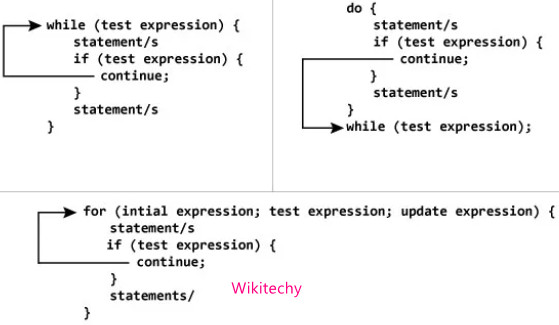
Continue
- This statement is used to bring the control to the beginning of the loop.
- The continue statement skips some lines of code inside the loop and continues with the next iteration.
- It is mainly used in a program for skiiping certain condition.
- This statement does not exit from the loop of the body.
- It is not used to exit from the loop body.
- Continue statement is not used with switch statement.
- It can be used only with while, do while and for loop.
- When the control encounters continue statement,control automatically executes the remaining statements of the loop body.
Syntax
Sample Code
Output


