How HashMap Works in Java ?
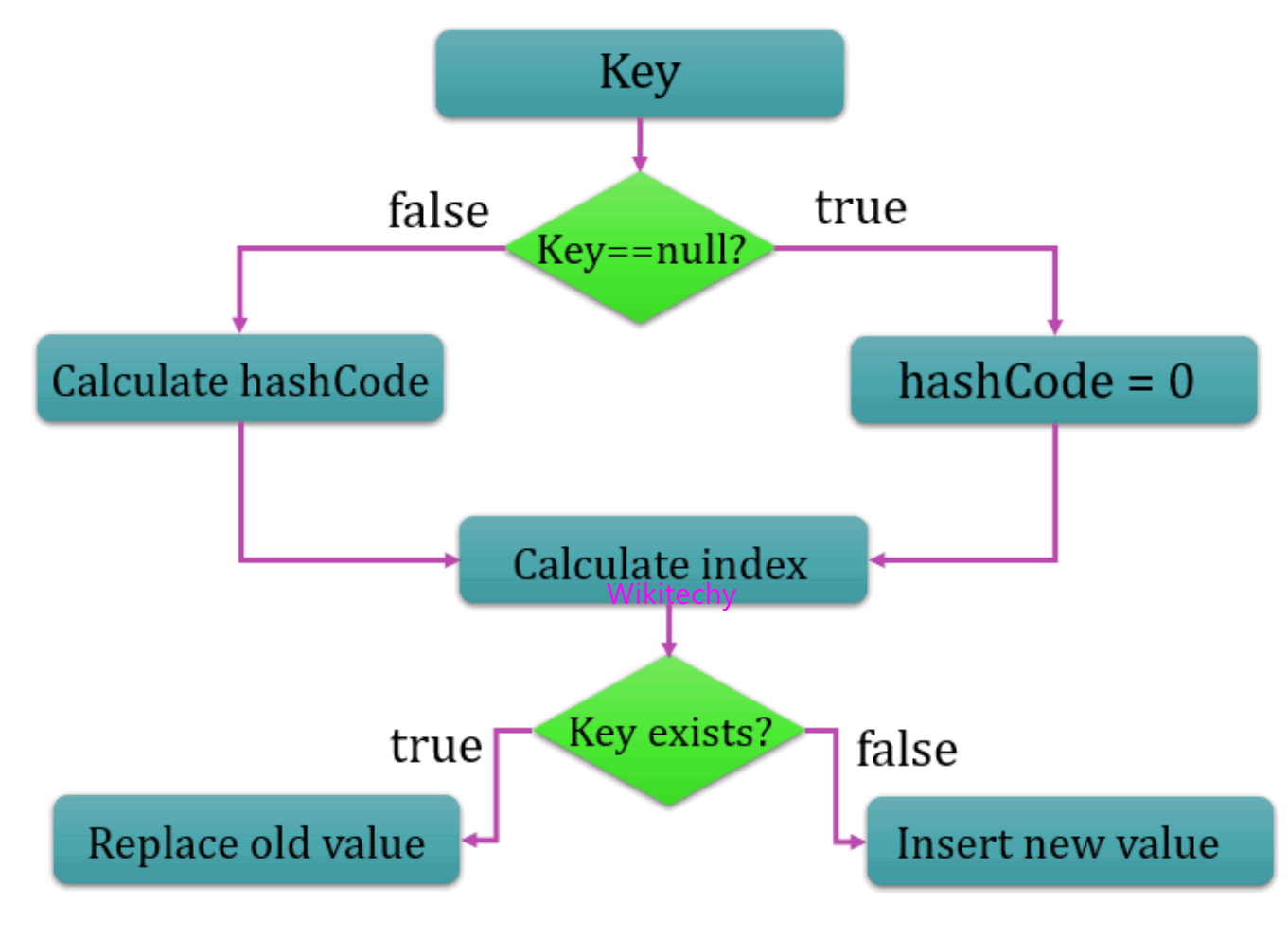
- HashMap is one of the most widly used implementation of Map to store key-value pairs. To implement HashMap with ArrayList.
- It is provides two basic HashMap functions they are: get(key) and put(key, value).
- While storing code to be checking the duplicate values. While duplicate values are presents to be removed.
- Implementation should not be used as a replacement of HashMap. Also while testing the code, make sure that the Object used in the KEY has proper implementation of equals() method.
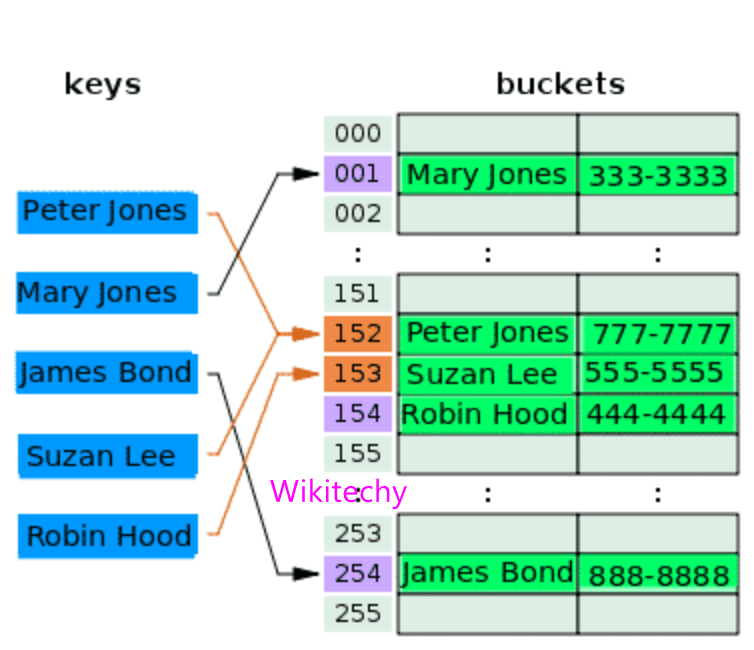
Example:
Output:
3
1
4
null