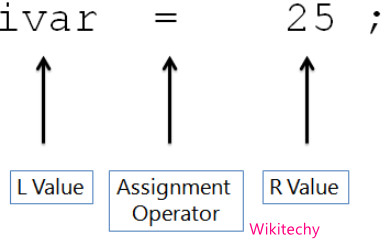
L Value
- L value or locator value represents an object that occupies some identifiable location in memory.
- In an assignment operator the l value can appear on right hand side or left hand side.
- Expression which refer to modifiable locations are called as “Modifiable L Values”.
- An incomplete type or constant attribute cannot have an array type of modifiable value attribute.
- Structures and Unions to be a modified lvalues, they should not contain any members with constant attribute.
- Storage location will be denoted by an identifier with name,value stored at a location will have the value of the variable.
- A lvalue identifier can be modified it refers to a memory location and if the type of it is arithmetic, structure, union or pointer.
- Example: If a pointer points to a storage region, then *ptr is a modifiable l value that allocates the storage region to which *ptr points.
- In C, this concept was termed “Locator Value”. And referred to expressions that locate objects.
The l-value is one of the following
- The name of the variable of any type i.e, an identifier of integral, floating, pointer, structure, or union type.
- A subscript ([ ]) expression that does not evaluate to an array.
- A unary-indirection (*) expression that does not refer to an array
- An l-value expression in parentheses.
- A constobject (a nonmodifiable l-value).
- The result of indirection through a pointer, provided that it isn’t a function pointer.
- The result of member access through pointer(-> or .)
R Value
- R- value refer to data value that is stored at some address in memory.
- R value is an expression that does not have a value assigned to it which means r value can either right side or left side of an assignment operator.