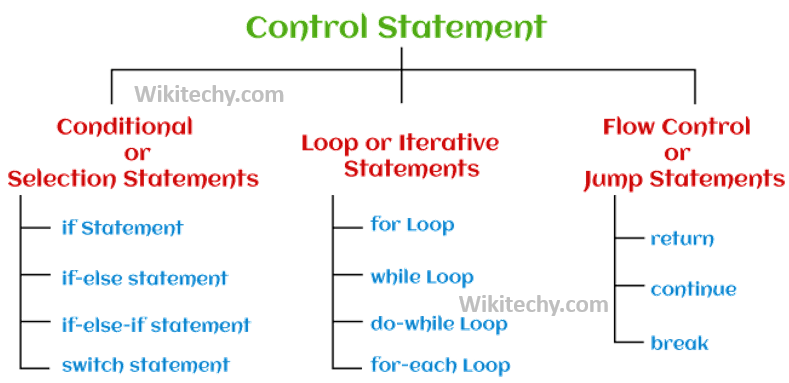
Java control statements are used to manage the flow of execution within a program. They can be categorized into three main types: selection, iteration, and jump statements.
1.Selection Statements
Selection statements allow the program to choose different paths of execution based on the result of a condition.
Definition:
These statements evaluate conditions to determine which block of code to execute.
Example:
public class DecisionMakingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 10;
// if statement
if (number > 0) {
System.out.println("The number is positive.");
}
// if-else statement
if (number % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("The number is even.");
} else {
System.out.println("The number is odd.");
}
// if-else-if ladder
if (number > 100) {
System.out.println("The number is greater than 100.");
} else if (number > 50) {
System.out.println("The number is greater than 50 but less than or equal to 100.");
} else {
System.out.println("The number is less than or equal to 50.");
}
// switch statement
int day = 3;
switch (day) {
case 1:
System.out.println("Monday");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("Tuesday");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("Wednesday");
break;
default:
System.out.println("Invalid day");
}
}
}
OUTPUT :
The number is positive.
The number is even.
The number is less than or equal to 50.
Wednesday
Features:
- Includes if, if-else , and switch statements.
- Allows decision-making based on conditions.
Advantages:
- Simplifies complex decision-making processes.
- Allows multiple outcomes based on different conditions.
Uses:
- Used to implement logic that depends on certain conditions, such as user input, validation, or state changes.
2.Iteration Statements (Loops)
Iteration statements repeat a block of code as long as a specified condition is true.
Definition:
These statements allow code to be executed repeatedly based on a condition.
Example:
public class LoopingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// for loop
System.out.println("For Loop:");
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
// while loop
System.out.println("\nWhile Loop:");
int j = 1;
while (j <= 5) {
System.out.println("j = " + j);
j++;
}
// do-while loop
System.out.println("\nDo-While Loop:");
int k = 1;
do {
System.out.println("k = " + k);
k++;
} while (k <= 5);
// Enhanced for loop
System.out.println("\nEnhanced For Loop:");
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int num : numbers) {
System.out.println("num = " + num);
}
}
}
OUTPUT :
For Loop:
i = 1
i = 2
i = 3
i = 4
i = 5
While Loop:
j = 1
j = 2
j = 3
j = 4
j = 5
Do-While Loop:
k = 1
k = 2
k = 3
k = 4
k = 5
Enhanced For Loop:
num = 1
num = 2
num = 3
num = 4
num = 5
Features:
- Includes for, while, and do-while loops .
- Executes a block of code multiple times.
Advantages:
- Reduces redundancy by reusing code.
- Useful for iterating through arrays, collections, or performing repeated calculations.
Uses:
- Used in scenarios where repetitive actions are required, such as processing data, traversing collections, or performing timed tasks.
3.Jump Statements
Jump statements are used to change the normal flow of execution.
Definition:
These statements move control to another part of the program.
Example:
public class JumpStatementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// break statement
System.out.println("Break Example:");
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
if (i == 3) {
break; // Exit loop when i == 3
}
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
// continue statement
System.out.println("\nContinue Example:");
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
if (i == 3) {
continue; // Skip the current iteration when i == 3
}
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
// return statement
System.out.println("\nReturn Example:");
printMessage(5);
printMessage(-1); // This will return early
}
public static void printMessage(int number) {
if (number < 0) {
System.out.println("Invalid number. Returning early.");
return; // Exit the method
}
System.out.println("The number is " + number);
}
}
OUTPUT :
Break Example:
i = 1
i = 2
Continue Example:
i = 1
i = 2
i = 4
i = 5
Return Example:
The number is 5
Invalid number. Returning early.
Features:
- Includes break, continue, and return statements.
- Alters the flow of control immediately.
Advantages:
- Allows for better control of the loop’s execution.
- Provides a way to exit or skip iterations without going through the complete cycle.
Uses:
- Used in loops or switch statements to exit or skip certain iterations based on specific conditions.








