1.Definition:
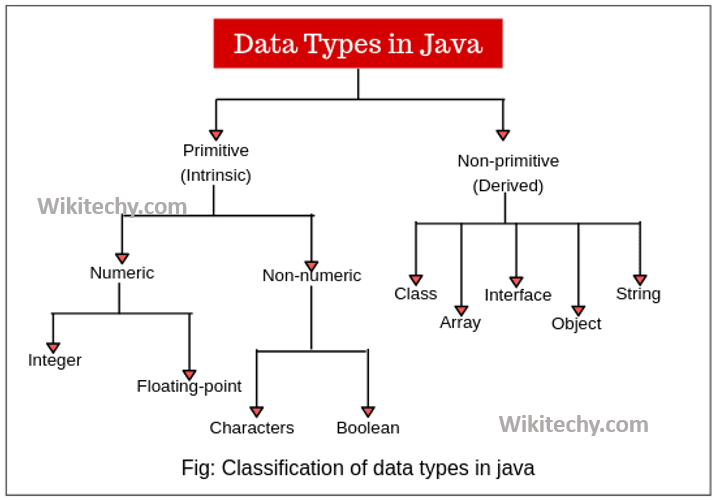
- Primitive Data Types: These are the most basic data types in Java , predefined by the language itself. They specify the size and type of variable values, and there are eight primitive data types.
- Non-Primitive Data Types (Reference Types): These are user-defined types and refer to objects. They are created using classes, interfaces, and arrays .
2.Types and Example:
A.Primitive Data Types:
1.byte:
-
- Example: byte age = 25;
- Range: -128 to 127
- Size: 1 byte (8 bits)
- Usage: Useful for saving memory in large arrays where memory savings are needed.
2.short:
-
- Example: short temperature = 1000;
- Range: -32,768 to 32,767
- Size: 2 bytes (16 bits)
- Usage: Used for medium-range integers.
3.int:
-
- Example: int salary = 50000;
- Range: -2^31 to 2^31-1
- Size: 4 bytes (32 bits)
- Usage: Commonly used for integer variables in Java programs.
4.long:
-
- Example: long distance = 100000000L;
- Range: -2^63 to 2^63-1
- Size: 8 bytes (64 bits)
- Usage: Useful when a larger range than int is required.
5.float:
-
- Example: float price = 19.99f;
- Range: ~1.4e-45 to 3.4e38
- Size: 4 bytes (32 bits)
- Usage: Used for fractional numbers requiring less precision.
6.double:
-
- Example: double weight = 70.5;
- Range: ~4.9e-324 to 1.8e308
- Size: 8 bytes (64 bits)
- Usage: Used for decimal numbers needing more precision than float.
7.char:
-
- Example: char grade = ‘A’;
- Range: 0 to 65,535 (UNICODE characters)
- Size: 2 bytes (16 bits)
- Usage: Used to store single characters.
8.boolean:
-
- Example: boolean isStudent = true;
- Values: true or false
- Size: Depends on JVM, but usually 1 bit.
- Usage: Used for true/false conditions
B.Non-Primitive Data Types (Reference Types):
1.String:
-
- Example: String name = “John”;
- Description: Represents a sequence of characters.
- Usage: Used to store text data.
2.Arrays:
-
- Example: int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3};
- Description: Represents a collection of variables of the same type.
- Usage: Used for storing multiple values in a single variable.
3.Classes and Objects:
-
- Example:
- class Person {String name;
int age;
}
Person person1 = new Person();
-
- Description: Defines the blueprint of an object in Java.
- Usage: Used to define custom types (objects) that hold multiple related fields and methods.
4.Interfaces:
-
- Example:
- interface Drawable {void draw();
}
-
- Description: Defines a contract that classes must follow by implementing specific methods.
Features:
- Primitive Data Types:
- Fixed size and predefined by Java.
- Directly store values, not references.
- Simple and efficient, offering fast performance.
- Non-Primitive Data Types:
- Can store multiple values or more complex data.
- Objects are created from these data types, and they store references, not actual values.
- Allow flexibility in designing programs with custom types.
Advantages:
- Primitive Data Types:
- Faster because they hold the actual values.
- Less memory overhead compared to objects.
- Non-Primitive Data Types:
- More versatile, allowing the creation of complex data structures like strings , arrays, and objects.
- Support rich functionalities through built-in methods (e.g., String has methods like length() and substring()).
Uses:
- Primitive Data Types:
- int: Used for counting, loops, array indices, etc.
- boolean: Used for conditions in control flow (if, while, etc.).
- char: Used for handling characters, e.g., processing text.
- Non-Primitive Data Types:
- String: Used in applications for text processing, input/output, and user interaction.
- Arrays: Used when handling multiple items of the same type, e.g., storing a list of numbers.
- Objects: Used to represent entities in object-oriented programming (OOP), such as a Person or Car in a simulation.